Machine translation (MT) has come a long way, but it’s still not perfect. As a translator, you might wonder if it’s worth using MT in your workflow.
In this post, we’ll delve into the pros and cons of using MT, provide tips on how to use it effectively, and discuss the ethical implications of relying on AI-powered translation.
1. Advantages of Using Machine Translation
Increased Productivity
- Faster Turnaround Times: MT can significantly speed up the translation process by generating initial drafts quickly.
- Reduced Manual Effort: By automating the translation of large volumes of text, MT can reduce the workload for human translators.
- Parallel Processing: MT tools can process multiple documents simultaneously, further increasing efficiency.
Language Barrier Reduction
- Global Reach: MT can help businesses and organizations reach a global audience by breaking down language barriers.
- Cross-Cultural Communication: MT can facilitate communication and collaboration between people from different cultural backgrounds.
- Accessibility: MT can make information accessible to people with language barriers, improving inclusivity.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Reduced Translation Costs: MT can significantly reduce translation costs, especially for large-volume projects.
- Scalability: MT can handle a large volume of translations without requiring additional human resources.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By accelerating the translation process, MT can help businesses launch products and services faster.
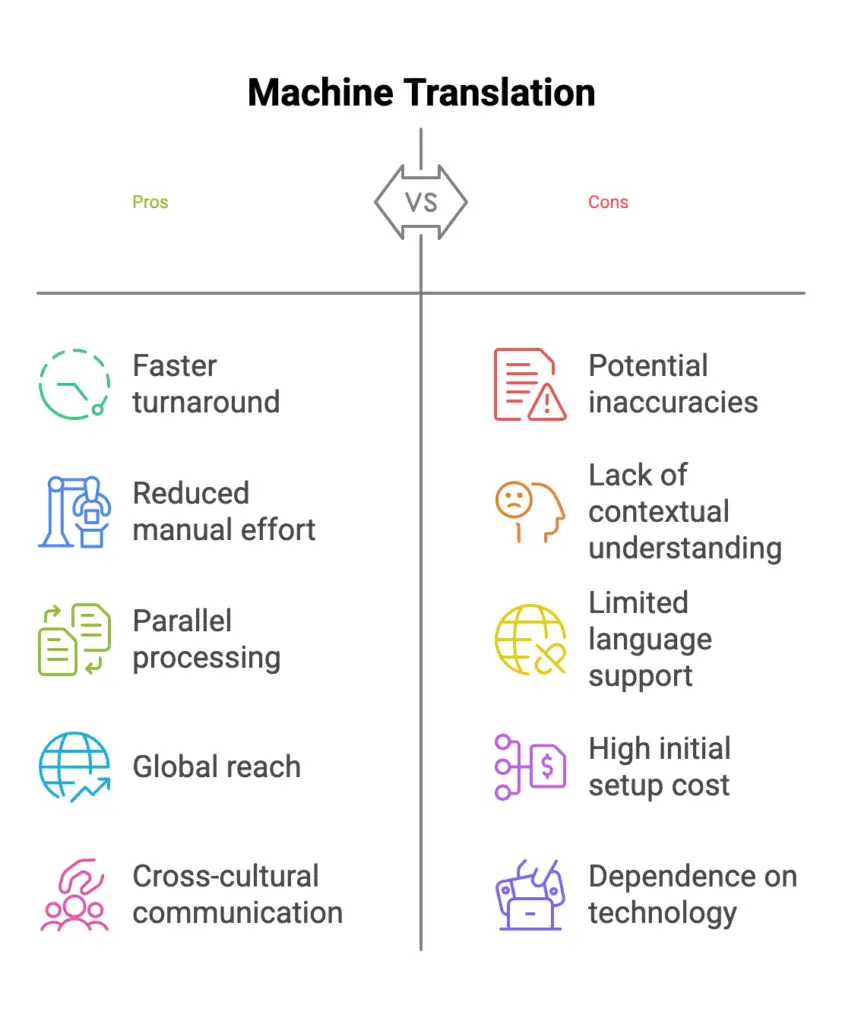
2. Limitations of Machine Translation
While machine translation (MT) has made significant strides, it still has limitations that can impact the quality and accuracy of translations. Here are some key disadvantages:
Quality Issues
- Inaccuracy and Nonsensical Translations: MT often struggles with complex sentences, idioms, and cultural references, leading to inaccurate or nonsensical translations.
- Lack of Contextual Understanding: MT tools may not fully grasp the context of a text, resulting in mistranslations.
- Technical Terminology: MT can be particularly challenging for technical documents, as it may not accurately translate specialized terms and jargon.
Cultural Nuances
- Misinterpretation of Idioms and Expressions: MT may misinterpret idioms and cultural references, leading to misunderstandings or unintended humor.
- Loss of Nuance and Tone: MT can struggle to capture the nuances of language, such as sarcasm, irony, and humor.
Ethical Concerns
- Plagiarism and Copyright Infringement: Overreliance on MT can lead to unintentional plagiarism or copyright infringement if not used responsibly.
- Transparency and Accountability: It’s important to be transparent about the use of MT and to ensure that the final translation is accurate and reliable.
- Potential for Misinformation: Inaccurate translations can spread misinformation and lead to misunderstandings.
3. Choosing the Right Machine Translation Tool
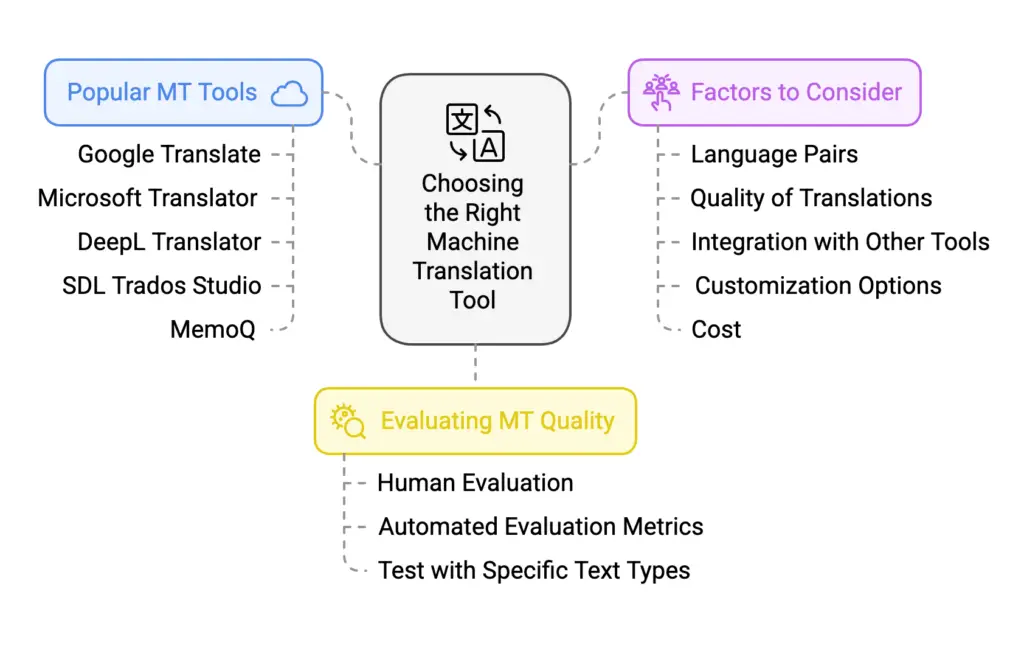
Popular MT Tools and Their Features
The translation technology market is constantly evolving, with numerous MT tools available. Some of the most popular options include:
- Google Translate: A widely-used free tool that offers translation in over 100 languages.
- Microsoft Translator: Another popular free tool that provides translation services across multiple platforms.
- DeepL Translator: Known for its high-quality translations, especially for European languages.
- SDL Trados Studio: A professional translation software suite that includes MT capabilities.
- MemoQ: A powerful translation memory tool that also offers MT integration.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an MT Tool
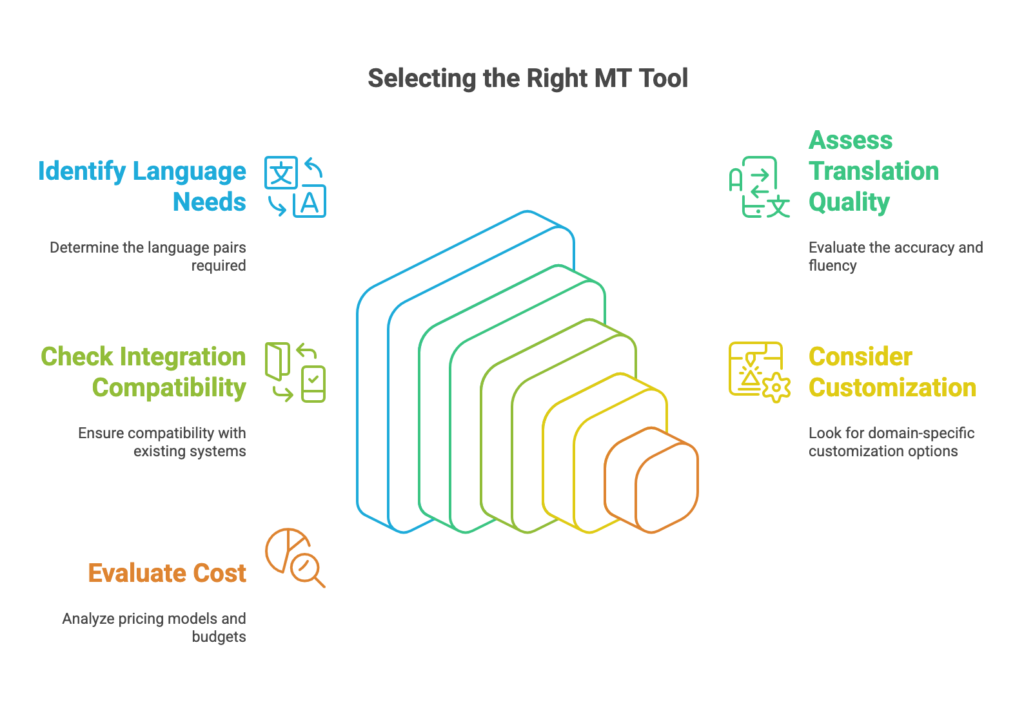
When choosing an MT tool, consider the following factors:
- Language Pairs: Ensure the tool supports the language pairs you frequently work with.
- Quality of Translations: Evaluate the accuracy and fluency of the tool’s translations, especially for specialized or technical texts.
- Integration with Other Tools: Consider the tool’s compatibility with your existing translation workflow and software.
- Customization Options: Look for tools that allow you to customize the MT engine with domain-specific terminology and style guides.
- Cost: Evaluate the pricing model and licensing options to determine the best fit for your budget.
Evaluating MT Quality and Accuracy
To assess the quality of an MT tool, you can use the following methods:
- Human Evaluation: Have human translators evaluate the quality of MT output and compare it to professional translations.
- Automated Evaluation Metrics: Use metrics like BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) and METEOR to measure the similarity between MT output and human reference translations.
- Test with Specific Text Types: Test the tool with different types of text, such as technical documents, literary texts, and marketing materials, to assess its performance.
4. Effective Post-Editing Techniques
The Role of Post-Editing in Improving MT Output
Post-editing is a crucial step in the machine translation process. It involves reviewing and correcting MT output to ensure accuracy, fluency, and cultural appropriateness. By carefully editing and refining MT-generated text, translators can significantly improve the quality of the final translation.
Best Practices for Efficient Post-Editing
To maximize efficiency and accuracy in post-editing, consider the following best practices:
- Understanding the MT Tool’s Strengths and Weaknesses: Familiarize yourself with the capabilities and limitations of the MT tool you’re using.
- Prioritizing Text Segments: Focus on editing the most challenging parts of the text, such as technical terms, cultural references, and complex sentence structures.
- Using Keyboard Shortcuts and Automation Tools: Utilize keyboard shortcuts and automation tools to streamline the post-editing process.
- Leveraging Translation Memory and Terminology Databases: Refer to these resources to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Collaborating with Other Translators: Consult with colleagues or subject matter experts to resolve difficult passages.
Quality Assurance Checks and Guidelines
To ensure the highest quality of post-edited translations, implement the following quality assurance checks:
- Proofreading: Carefully review the edited text for any errors in grammar, punctuation, or spelling.
- Style and Tone: Ensure that the translated text adheres to the appropriate style guide and tone.
- Cultural Nuances: Verify that cultural references and idioms are accurately translated.
- Terminology Consistency: Check for consistent use of terminology throughout the document.
- Client-Specific Guidelines: Adh
5. Leveraging MT for Specific Translation Tasks
Using MT for Initial Drafts and Rapid Translation
- Quick Turnaround: MT can generate initial drafts quickly, allowing for faster project completion.
- Identifying Key Points: MT can help identify the main points and overall context of a text.
Utilizing MT for Large-Scale Projects and Repetitive Tasks
- Handling Large Volumes: MT can efficiently process large volumes of text, reducing manual effort.
- Standardizing Terminology: MT can help maintain consistency in terminology across multiple documents.
Combining MT with Human Translation for Hybrid Approaches
- Post-Editing: Human translators can refine MT output to achieve high-quality translations.
- Machine-Assisted Translation (MAT): MT can be used as a tool to assist human translators, improving their efficiency and productivity.
- Translation Memory Integration: MT can be integrated with translation memory systems to leverage past translations and improve consistency.
6. How to Use Machine Translation Ethically and Effectively
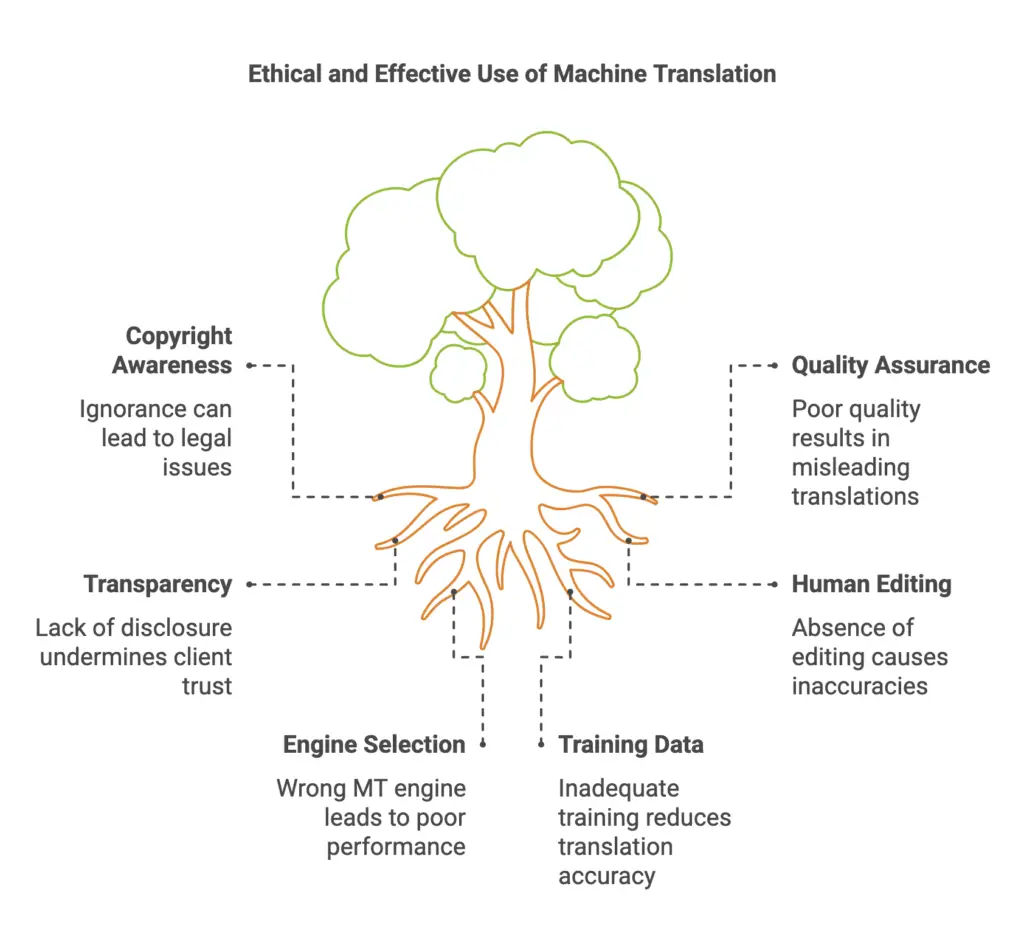
Fair Use and Copyright Laws
When using MT, it’s essential to be aware of copyright laws and fair use principles. Always ensure that you have the necessary rights to use the source text and that your use of MT complies with copyright regulations.
Ethical Implications of Using MT
- Quality Assurance: It’s crucial to maintain high quality standards when using MT. Avoid overreliance on MT, as it can lead to inaccurate and misleading translations.
- Transparency: Be transparent with your clients about the use of MT in your workflow. Disclose the extent of MT usage and the level of human involvement.
- Client Expectations: Clearly communicate the limitations of MT and manage client expectations.
Transparency and Disclosure of MT Usage
- Client Communication: Be open with your clients about your use of MT and the potential benefits and limitations.
- Industry Standards: Adhere to industry standards and guidelines for the use of MT.
- Ethical Guidelines: Follow ethical guidelines and avoid misrepresenting the extent of human involvement in the translation process.
Human Editing is Essential
- Post-Editing: Always have a human translator review and edit MT output to ensure accuracy, fluency, and cultural appropriateness.
- Quality Assurance: Implement rigorous quality control measures to identify and correct errors.
Choose the Right MT Engine
- Language Pair Compatibility: Select an MT engine that supports the specific language pairs you need.
- Domain Specialization: Consider using domain-specific MT engines for specialized texts.
- Customization Options: Look for tools that allow you to customize the MT engine with your specific terminology and style guidelines.
Train Your MT Engine
- Domain-Specific Training Data: Provide the MT engine with domain-specific training data to improve its accuracy.
- Style Guide Integration: Incorporate style guides into the training data to ensure consistency.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly update and refine the training data to keep pace with language evolution.
Use MT as a Tool, Not a Replacement
- Initial Draft Generation: Use MT to generate initial drafts, saving time and effort.
- Large-Scale Projects: MT can be helpful for large-scale projects, especially for repetitive tasks.
- Hybrid Approach: Combine MT with human translation to achieve optimal results.
7. The Future of Translation
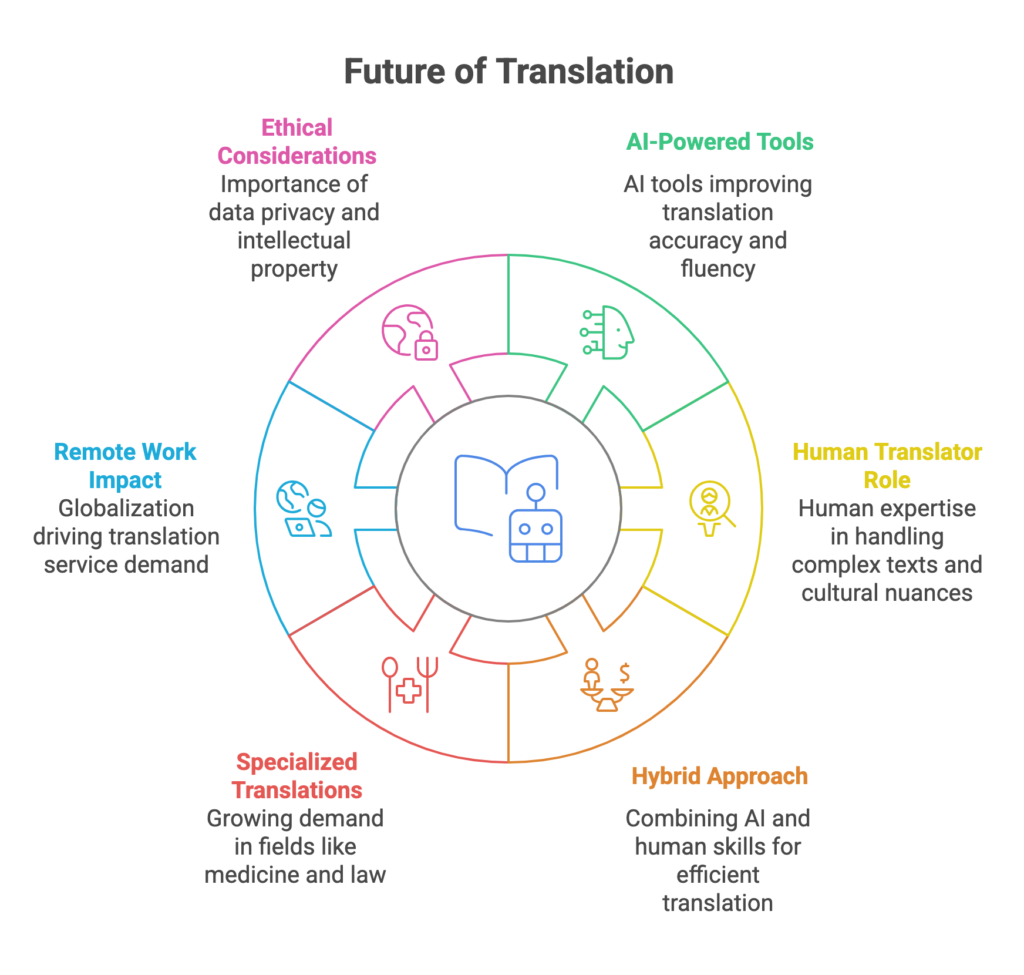
The Rise of AI-Powered Translation Tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly advancing, and its impact on machine translation is significant. We can expect to see further improvements in the accuracy and fluency of MT tools. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to learn and adapt, leading to more sophisticated and nuanced translations.
The Role of Human Translators in the Age of AI
While MT has made significant strides, human translators will continue to play a vital role in the translation industry. Human expertise is essential for handling complex texts, cultural nuances, and specialized terminology. Human translators can also provide valuable insights into the target audience and tailor the translation accordingly.
The Future of the Translation Industry
The future of the translation industry is likely to involve a hybrid approach, combining human expertise with machine translation. As MT technology continues to improve, human translators will focus on higher-value tasks, such as post-editing, localization, and content creation.
Key trends in the translation industry include:
- Increased Demand for Specialized Translations: As globalization continues, there will be a growing demand for specialized translations in fields like medicine, law, and technology.
- Remote Work and Globalization: Remote work and globalization will continue to drive the demand for translation services.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations, such as data privacy and intellectual property rights, will become increasingly important.
Conclusion
MT is a tool, not a replacement for human expertise. Understand the limitations and strengths of machine translation, to effectively leverage this technology to improve translation workflow and deliver high-quality translations. Also, it’s important to use it responsibly and ethically.