Becoming a skilled translator requires more than language proficiency.
It’s about mastering a set of core skills that ensure accuracy, efficiency, and cultural relevance. Whether you’re just starting your translation career or looking to refine your abilities, certain competencies can set you apart.
In this article, we’ll break down the ten essential skills every aspiring translator should develop to succeed in the competitive world of translation.
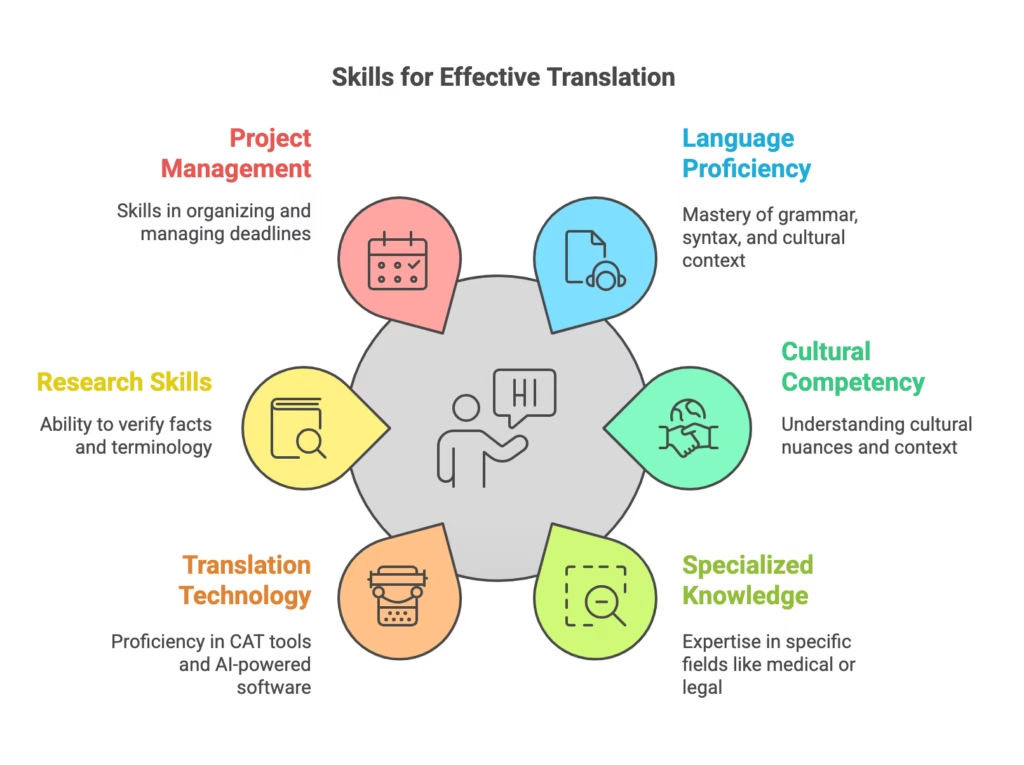
1. Advanced Language Proficiency
A translator must possess an exceptional command of both the source and target languages, going beyond basic fluency to understand nuances and subtleties in each language. This involves:
- Mastering Grammar & Syntax: Be well-versed in the grammatical rules and sentence structures of both languages to ensure accuracy and clarity in your translations.
- Understanding Idiomatic Expressions & Regional Dialects: Know how to translate idioms, phrasal verbs, and colloquial expressions so they sound natural and culturally appropriate in the target language.
- Fluency in Both Written & Spoken Forms: Being able to read and write fluently in both languages, and understanding spoken language (including accents and slang), is critical. This enables you to accurately convey the message without losing meaning.
2. Cultural Competency
Language and culture are inseparable, and a translator must be aware of cultural contexts that shape communication. To excel, a translator should:
- Adapt Tone and Style Based on Cultural Context: Understand that a direct translation may not always convey the intended meaning or tone. The style, humor, and emotional weight of words can change based on cultural context.
- Be Aware of Slang, Humor, and Historical References: Know when certain phrases or jokes may not have an equivalent in the target language or could be inappropriate.
- Avoid Mistranslations That May Lead to Misunderstandings or Offense: Understand cultural sensitivities to avoid translating content that could inadvertently offend, especially in legal, marketing, and literary texts.
3. Expertise in Specialized Fields
Translation isn’t a one-size-fits-all skill. It’s crucial to specialize in one or more areas to gain a competitive edge. Specializing allows you to:
- Choose a Niche (Legal, Medical, Technical, etc.): Each niche has its own terminology, standards, and writing styles, so becoming an expert in a field can increase your chances of landing higher-paying, long-term clients.
- Stay Updated with Industry-Specific Terminology: Industry jargon evolves, so continuous learning and staying informed about changes in terminology and practices are essential.
- Conduct In-Depth Research for Accuracy: Specialization often requires deep research and understanding of the subject matter to ensure accurate and precise translations, especially in technical, medical, or legal documents.
4. Proficiency in CAT Tools & Translation Technology
With the rise of technology, translation tools have become vital in ensuring quality, speed, and consistency. To leverage these tools effectively, a translator should:
- Familiarize Yourself with Tools like SDL Trados, MemoQ, and Smartcat: These tools help improve productivity by storing previous translations for future use (Translation Memory) and ensuring consistency across large projects.
- Utilize Translation Memory (TM) for Efficiency: Translation Memory stores past translations and suggests them when a similar sentence is encountered in future texts. It’s essential for maintaining consistency and speeding up the process.
- Stay Updated on Emerging AI-Powered Translation Tools: AI tools such as machine translation (MT) and neural machine translation (NMT) are becoming integral to the translation industry, so understanding how to use them effectively and when post-editing is necessary is crucial.
5. Excellent Research Skills

Translation is akin to detective work—verifying facts, terminology, and context is essential to ensuring accuracy. A translator should:
- Use Dictionaries, Glossaries, and Trusted Reference Materials: Rely on specialized dictionaries and glossaries, especially for technical or legal fields, and use multiple resources to confirm meaning and context.
- Fact-Check Using Reputable Sources: Research is key in translating terms, especially when dealing with new or unfamiliar topics.
Cross-Reference Multiple Resources for Accuracy: Don’t rely on a single source. Check multiple sources to ensure the accuracy of the translation.
6. Project Management and Organizational Skills
Freelance translators often juggle multiple projects and deadlines. To thrive, they must:
- Plan Work Effectively and Set Realistic Deadlines: Set clear, manageable goals to ensure timely delivery of high-quality work.
- Use Project Management Tools like Trello or Asana: These tools can help track tasks, deadlines, and communication with clients, making it easier to manage multiple projects.
- Prioritize Tasks and Balance Multiple Assignments: Learn how to balance several ongoing projects by setting priorities, managing your time, and avoiding over-commitment.
7. Strong Writing and Editing Abilities
Translations should flow naturally in the target language, making writing and editing skills crucial for high-quality work:
- Ensure Clarity, Coherence, and Natural Flow: A translation should not feel like a translation; it should feel like an original text written in the target language.
- Adapt Writing Style Based on Audience and Purpose: Whether translating for a legal document, marketing campaign, or literary work, adjust tone, style, and vocabulary based on the intended audience.
- Proofread for Grammar, Spelling, and Punctuation Errors: Always go over your work with a fine-tooth comb to avoid simple errors that could damage your credibility.
8. Attention to Detail & Quality Control

In translation, every word matters. A small mistake can alter the meaning of a sentence, which is why attention to detail is crucial. To ensure the highest quality translation, focus on:
- Double-Check Terminology and Consistency: Ensure consistent use of terms across the entire text, especially in technical or legal fields. Using the correct terminology is key to providing a professional translation.
- Implement Quality Assurance Checks Before Delivery: Before submitting your work, always run a final check to ensure there are no overlooked mistakes. This includes reviewing for missing or extra words, typos, and formatting issues.
- Look for Errors, Omissions, and Formatting Issues: A careful final review will catch mistakes that may have slipped through during the translation process. This is especially important for documents with complex formatting or long sentences.
9. Time Management & Productivity
Freelance translators often work with tight deadlines and multiple projects on the go, making effective time management a key to success. To stay productive and maintain high-quality work:
- Set Daily or Weekly Work Goals: Break down your projects into smaller, manageable tasks, and set realistic deadlines for each. This will keep you on track and help avoid last-minute panic.
- Use Productivity Tools to Streamline Tasks: Utilize task management apps like Todoist, RescueTime, or Pomodoro timers to structure your work and stay focused. These tools can help minimize distractions and ensure that you make the most of your time.
- Avoid Burnout by Balancing Workload and Breaks: Working non-stop can lead to fatigue and decreased productivity. Schedule regular breaks, and ensure you have time to recharge so you can stay fresh and motivated.
10. Continuous Professional Development
The translation industry is evolving rapidly with new technologies, tools, and trends emerging regularly. To stay competitive, translators must prioritize continuous professional development. Here’s how you can do it:
- Participate in Industry Webinars, Courses, and Certifications: Stay updated by attending webinars, taking online courses, or earning certifications. This not only improves your skills but also increases your credibility as a professional translator.
- Stay Updated with Translation Technology Advancements: Keep up with the latest developments in CAT tools, AI, and machine translation. By understanding and mastering these new technologies, you’ll be able to offer cutting-edge services to clients.
Network with Peers and Join Professional Associations: Join translation organizations such as the ATA (American Translators Association) or ITI (Institute of Translation and Interpreting). Networking with peers will help you stay informed about industry trends, job opportunities, and best practices.
Common Questions About Becoming a Translator
Q: What qualifications do I need to become a translator?
A: While a formal degree in translation can be beneficial, it’s not always mandatory. Many successful translators have degrees in other fields and develop their skills through experience and specialized training. Strong language proficiency, cultural competency, and the skills outlined in this article are essential.
Q: How long does it take to become a proficient translator?
A: There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on your language skills, dedication, and the complexity of the translation work you pursue. Building expertise takes time and continuous learning.
Q: How do I find translation jobs as a beginner?
A: Networking, creating a strong online presence (e.g., a LinkedIn profile or portfolio website), and reaching out to translation agencies or potential clients are good starting points. Consider volunteering for translation projects to gain experience.
Q: What is the difference between a translator and an interpreter?
A: Translators work with written text, while interpreters work with spoken language. These are distinct skill sets, although some professionals may do both.
Q: Is it necessary to specialize in a specific field of translation?
A: While not always required, specializing can definitely enhance your career prospects and allow you to command higher rates. It demonstrates expertise and makes you more attractive to clients in that niche.
Q: How much do translators earn?
A: Translator salaries vary widely depending on experience, specialization, language combination, and location. Freelance translators often charge per word or per hour, while in-house translators may have a fixed annual salary. Researching industry rates and negotiating effectively are important.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid as a translator?
A: Some common mistakes include relying too heavily on machine translation without proper editing, neglecting cultural context, failing to proofread carefully, and not managing time effectively.
Q: How important is continuing education for translators?
A: Continuing education is crucial in the ever-evolving translation industry. Staying updated with new technologies, industry trends, and best practices is essential for maintaining your skills and competitiveness.